Verbs express actions (physical or mental), and also states or occurrences. In Spanish, these words are conjugated in four modes namely: indicative (indicativo), subjunctive (subjuntivo), conditional (condicional) and imperative (imperativo)
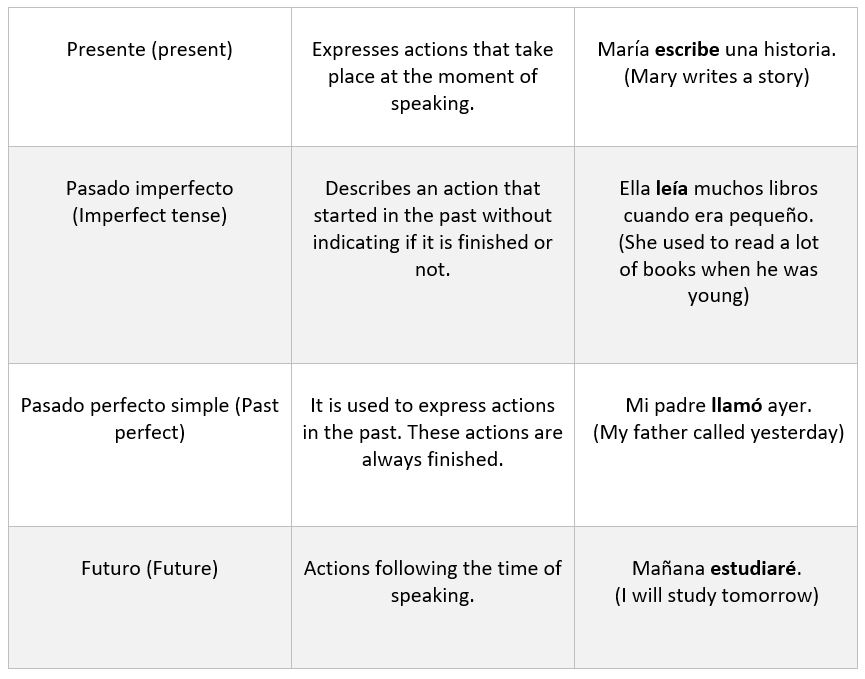
- Modo indicativo (Indicative mode): is used to express what is (present tense), what was (past tense), what will be (future tense).
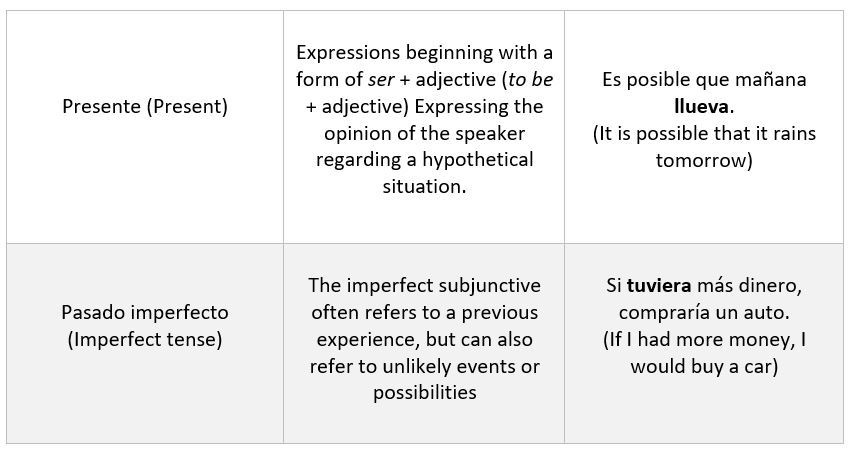
- Modo subjuntivo (Subjunctive mode):
These are the concepts that are hypothetical. On the other hand, those which embody the expression of feelings of the speaker towards a state or an action.
- Modo condicional (Conditional mode):
It expresses uncertainty or probability in conditional sentences. For instance:
Si yo estudiara más, sacaría mejores notas.
(If I studied more, I would get better grades)
Si durmiera más, me sentiría mejor.
(If I slept more, I would feel beter)
Si no lloviera, iría al parque.
(If it did not rain, I would go to the park)
- Modo imperativo (Imperative mode):
Imperative sentences mostly express an order or prohibition. For instance:
Siéntate
(Sit down)
¡No lo hagas!
(Don’t do it!)
¡Haz la tarea!
(Do your homework!)
